In the research of the Radio-Photoluminescence (RPL) glass dosimeter, a research team from the Laboratory for High Power Laser Components of the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) found that the prepared and developed Ag-Nd co-doped phosphate glass can be applied to RPL glass dosimeters and proved to be a multi-wavelength RPL fluorescent glass material. The related results were published in Materials under the title "Silver-Neodymium Codoped Lithium Aluminum Metaphosphate Glasses for Radio-Photoluminescence Dosimeter" on August 11, 2022.
Ag-doped phosphate RPL glass dosimeters generally use the radiation photoluminescence at the center of the Ag defect to achieve the calibration of the radiation dose, and its fluorescence intensity is proportional to the radiation dose. However, the calibration of single-wavelength fluorescence will be disturbed by the external environment, resulting in calibration error.
In this study, the research team successfully prepared an Ag-Nd co-doped phosphate glass compared to the traditional Ag-single-doped glasses used for RPL glass dosimeters. Under UV excitation, the RPL peak maximum intensity of the Ag defect center at 650 nm and the fluorescence peak intensities of Nd3+ ions at 882 nm and 1054 nm showed good linear relationship with the radiation dose. The linear slopes under excitation at 310 nm are 0.66, 2.08 and 3.44, respectively, and the energy transfer efficiency between Ag and Nd is about 25%. The linear slopes under excitation at 380 nm are 0.4, 1.41 and 2.26, respectively, and the energy transfer efficiency between Ag and Nd is about 50%. With good fluorescence response and high transfer efficiency, it is proved to be a multi-wavelength RPL glass material.

Figure 1. The fluorescence spectra of the Ag–Nd co-doped phosphate glasses at different radiation doses. (Image by SIOM)
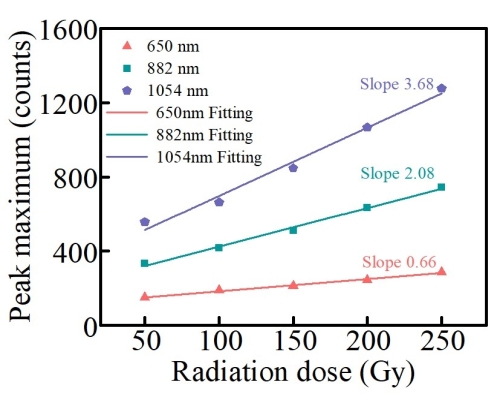
Figure 2. the linear relationship between the RPL peak maximum intensity of Ag defect centers at 650 nm and the fluorescence peak maximum intensity of Nd3+ ions at 882 and 1054 nm and the radiation dose in Ag–Nd co-doped phosphate glasses. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165527
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/