A research team from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) summarized the most recent progress in ultrafast Raman fiber lasers in a review paper. Three categories of ultrafast Raman fiber laser technologies have been reviewed, including mode-locking, synchronously-pumping and nonlinear optical gain modulation (NOGM). The results were published on PhotoniX on August 4, 2022.
Nowadays, in the aspects of pulse energy and du ration, mode-locked Raman fiber lasers are still not comparable to their rare-earth doped counterparts. It is mainly because long optical fiber is necessary to provide adequate Raman gain under the condition of CW pump. Ultrafast pulses generated in a long fiber cavity would experience large dispersion and nonlinearity, which limits the pulse energy, broadens the pulse duration, and narrows the working regime of single pulse operation.
The research team found that, since Raman gain coefficient is intensity-dependent, replacing CW pump with pulsed one could effectively increase Raman conversion efficiency, so as to solve the problem of long fiber cavity length in the case of mode-locked Raman fiber lasers. Currently, delay line based synchronously-pumping can produce Raman pulses with performance comparable to conventional rare-earth doped ultrafast fiber lasers. Yet, the involvement of delay line increases the cost and complexity of the system.
The leader of the research team said, “It is worth emphasizing that both mode-locked and synchronously-pumped Raman fiber lasers are based on oscillators.” Thus, for the sake of balance dispersion, nonlinearity, gain and loss inside fiber oscillators, their conventional output pulse energies are limited to the level of nJ.
Compared with mode-locking and synchronously-pumping, the method of NOGM avoids the oscillator structure, which gathers various advantages including simple structure, long-term stability, high pulse energy and short pulse duration. Simulations have confirmed that femtosecond Raman pulses with several MW peak power could be generated by NOGM.
Researchers believe, in the near future, the experimental performances of fiber-based NOGM lasers are expected to be improved, which have the ability to generate wavelength-agile, femtosecond laser pulses with μJ-level pulse energy under high optical efficiency.
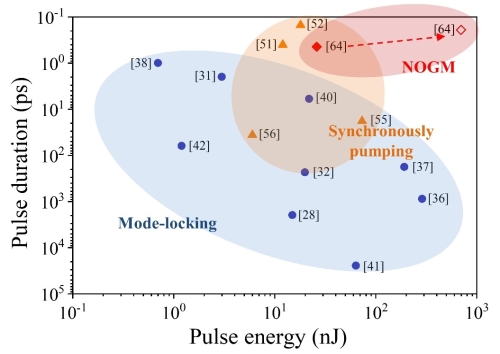
Fig. 1. Summary of the pulse energy and duration of the reported Raman fiber lasers, including mode-locking (blue circles), synchronously pumping (orange triangle) and NOGM (red diamond). (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43074-022-00064-2
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/