The Laboratory of Thin Film Optics of the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences make progress in the preparation of mixture-based quarter-wave plate laser beam splitter (PLBS) coatings to improve the performance of the coating. The corresponding research result is published in Optics & Laser Technology on June 28, 2022.
The plate beam splitters are widely used in quantum communication, measurement and laser systems due to their unique optical properties. On the one hand, the plate beam splitter used in high-power laser systems should achieve specific spectral performance; on the other hand, for the sake of meet the ever-increasing output power requirements of laser systems, the plate beam splitter also need to have a high laser damage threshold.
Mixture coating materials have attracted much attention in the field of high-power laser coatings in recent years because of their tunable refractive index and optical bandgap, and have been used in the design and preparation of coatings such as high-reflective coatings, polarizer coatings, and dichroic mirror coatings.
In order to obtain a specific intensity-splitting ratio, one or more non-quarter-wave layers are often required in the coating structure of the PLBS coatings, which leads to an increase in the electric field intensity and an increase in the difficulty of controlling the coating layer thickness.
The researchers realize the tuning of the mixture material by tuning the ratio of the two materials in it and then use the quarter-wave coating structure to realize the PLBS coating with arbitrary T/R ratios.
On the basis of studying the optical and mechanical properties of the mixture coatings under different mixture ratios, the properties of PLBS coatings are compared. Two mixture based PLBS coatings using HfO2–Al2O3 mixture material as high-n layer and SiO2 as low-n layer are experimentally demonstrated. Then, researchers compared the former two mixture based PLBS coatings with a traditional PLBS coating using HfO2 and SiO2 as high-n and low-n layers.
The above research results show that the mixture-based PLBS coatings have lower surface roughness, larger intensity-splitting bandwidth, and nearly doubles the laser damage threshold (1064 nm).
For applications with smaller bandwidth requirements, the laser damage threshold can be improved by a factor of ~2.6. Therefore, the PLBS coating prepared based on the mixture material can not only obtain more excellent performance, but also simplify the design and fabrication process.
The research team believe that the design strategies proposed in this study provide new insights for many laser fields that rely on high-quality PLBS coatings.
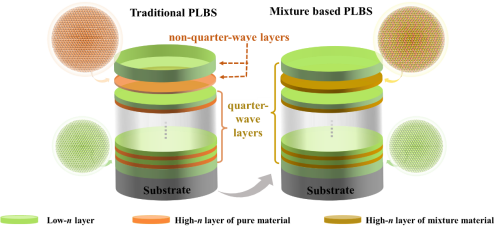
Fig. 1. Schematic of two types of PLBS coatings. (Image by SIOM)
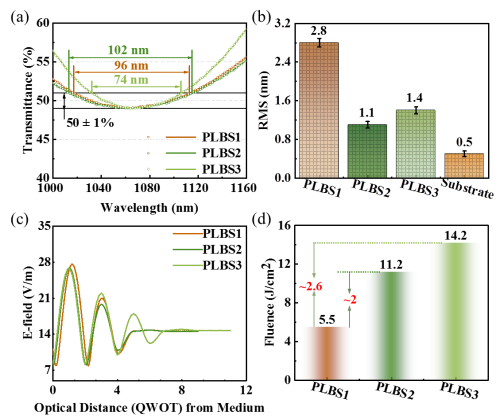
Fig. 2. Performance of PLBS coatings prepared by pure HfO2 material (PLBS1), HfO2–Al2O3 mixture materials with two different ratios (PLBS2 and PLBS3) as high refractive index materials, and low refractive index pure SiO2 materials. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108399
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/