Recently, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have reported that the gradient refractive index of SiO2 film was accurately controlled by using glancing angle deposition and discontinuous gradient rotation of substrate, and a high-performance SiO2 gradient refractive index ultra wideband antireflection film with ultra wideband, high damage threshold and uniform thickness was prepared. Relevant study has been published in Optical Materials Express on May 19, 2022.
In order to reduce the reflection on the surface of the optical elements, increase the transmittance of light in the working band, and obtain better optical performance, broadband antireflection films are widely used in many optical systems.
Traditional broadband anti-reflection films are prepared using high and low refractive index film stacks. The antireflection bandwidth it can achieve is limited by the refractive index of the material and the film stack, so it is difficult to achieve the antireflection effect in the ultra-wideband range. In the case of gradient index optics, by controlling the porosity, any ideal refractive index in the refractive index range of air and material can be achieved, which provides great flexibility for the development of ultra wideband antireflection films. However, due to the obvious non-uniformity of film thickness in the process of glancing angle deposition, the practicability of the films prepared by glancing angle deposition is greatly reduced.
To solve this problem, the research group designed a discontinuous gradient rotation scheme based on the refractive index control range of SiO2 film, and successfully developed a high-performance SiO2 gradient refractive index ultra wideband antireflection film with ultra wideband, high damage threshold, and uniform thickness by combining the electron beam inclined deposition technology. Its optical properties, such as residual reflectivity, thickness uniformity, and laser damage threshold, were tested, analyzed, and compared with the variable refractive index anti-reflection film without rotating speed and the traditional anti-reflection film. The average residual reflectance of the developed high-performance ultra wideband antireflection film can achieve an average value of 0.59% across a spectral range of 400-1800nm. By comparing the performance, the ultra-wideband anti-reflection film with substrate speed has higher stability compared with the broadband anti-reflection film without substrate speed and a higher damage threshold than the traditional anti-reflection film.
The research results can promote the application of ultra wideband antireflection films in high power laser systems.
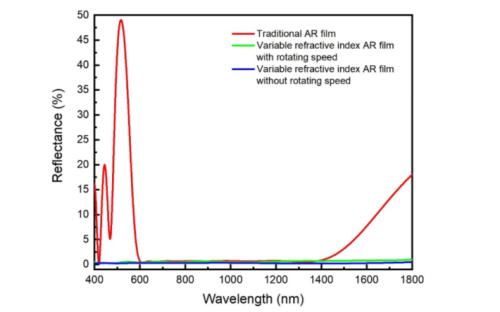
Figure1. The measure dresidual reflectance curve of the broadband antireflective film under three conditions. (Image by SIOM)
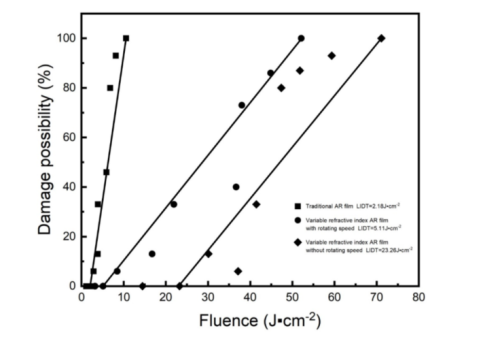
Figure 2. The laser-induced damage test (LIDT) for three types of anti-reflective films. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.459950
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/