A research group, led by Prof. Yan Feng from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has made research progress in the single frequency (SF) 589 nm fiber laser. The relevant result is published on Optics Express on March 14, 2022, which title is “Robust single-frequency 589 nm fiber laser based on phase modulation and passive demodulation".
It is well known that high-power 589 nm laser has important application in sodium laser guide star (LGS). The usual method to obtain high power SF 589 nm laser is Raman fiber amplification of 1178 nm seed laser and sequential frequency doubling. However, stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) severely limit the power scaling of single frequency or narrow linewidth Raman fiber amplifiers.
In this research, a {0,π} binary phase modulation is applied to the 1178 nm single frequency diode seed laser before the fiber amplifier to broaden the laser linewidth and suppress SBS. 49 W 1178 nm laser of linewidth 800 MHz is produced with an optical conversion efficiency of 53.6% from 1120 nm to 1178 nm.
After single-pass frequency doubling in a PPSLT crystal, 20 W 589 nm laser is obtained. The corresponding doubling efficiency is 41.6%. Owing to the phase doubling effect in second harmonic generation, the 589 nm laser spectrum is compressed back to single frequency in the SHG process. To the best of our knowledge, it is the highest power reported for CW 589 nm laser generation by single-pass frequency doubling.
This approach significantly simplifies the sodium guide star laser design and improves robustness. Due to the flexible wavelength of Raman, it can be further expanded to obtain single-frequency lasers of other wavelengths.
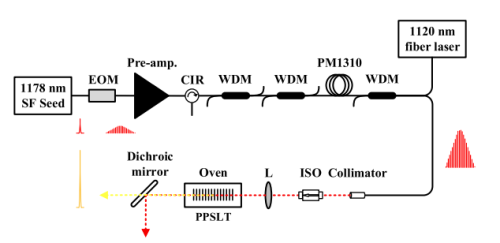
Fig. 1. The experimental setup. (Image by SIOM)
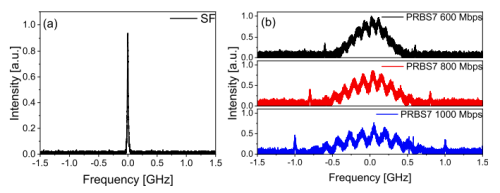
Fig. 2. The spectra of the 1178 nm laser. (a) without modulation. (b) with PRBS7 modulation of 600 Mbps, 800 Mbps and 1000 Mbps bit rates respectively. (Image by SIOM)
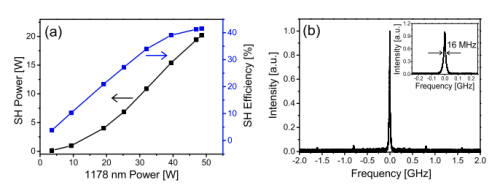
Fig. 3. (a) SH output power and conversion efficiency as a function of 1178 nm laser power, (b) Spectrum of the SH output laser at the highest output power (20 W). Inset: fine spectra of output laser. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.454139
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/