Recently, researchers from the State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics in Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have made new progress in the angular momentum properties of quantum vortex scattering and the manipulation of the quantum states of high-energy particles. The relevant results were published in Physical Review D on October 25 and Physical Review Research on December 7, 2021.
It is well known that, in quantum field theory established in the 1940s, the field quantization is usually performed by expanding fields with the basis of plane waves. This theoretical framework has achieved great success in high-energy particle physics in the past 70 years. Nonetheless, the angular momentum properties in the high-energy scattering process have never been self-consistently solved, because the plane waves do not carry the intrinsic orbital angular momentum (OAM).
On the other hand, the vortex light and particle beams have been the research hot topics for 30 years. However, up to now, all the experimental schemes of generating, detecting, and manipulating the vortex beams are only applicable to the low-energy particles. The experimental generation and manipulation of high-energy vortex particles are very challenging since their wavelength is orders of magnitudes smaller, so a new breakthrough in both theory and experimental method for high-energy particles is needed.
Based on the theory of quantum electrodynamics (QED), researchers performed the field quantization with the basis of quantum vortex states (Bessel modes), and successfully developed a complete theory to describe the high-energy vortex scattering. The quantum vortex states carry well-defined intrinsic OAM, thus this theory can satisfactorily solve the angular momentum conservation, conversion, and spin-orbit interaction in the QED vortex scattering.
Compared with the plane-wave scattering, the momentum spectrum of vortex scattering is significantly broadened, because the resonance strictly determined by four-momentum conservation is replaced by the conservation of energy and longitudinal momentum. More importantly, for the first time, the new theory gives the OAM spectrum for the vortex scattering process.
Additionally, researchers proposed a new scheme of generating the high-energy vortex positron beam with intrinsic OAM via Beth-Heitler process, and then developed a new mechanism of manipulating the quantum states of high-energy particles based on the vortex scattering process.
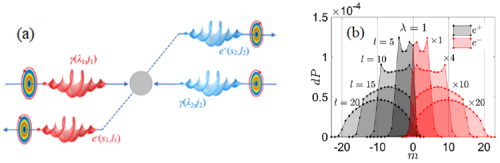
Figure 1. (a) Schematic diagram of quantum vortex scattering. (b) OAM spectrum of electrons and positrons generated in Beth-Heitler process. (Image by SIOM)
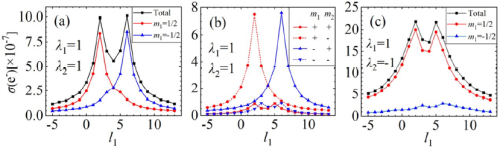
Figure 2. OAM spectra of electrons with different spin polarizations in Breit-Wheeler process. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.104.076025
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/