Quantum sensing with cold atoms is attracting increasingly attention in the research frontier of quantum technologies. Recently, the cold atom physics research team from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has made new experimental progress in the research of characterizing isotropic laser cooling’s properties. The related research results have been published in Optics Express on December 20, 2021.
Isotropic laser cooling in the form of obtaining cold atoms via diffuse reflection light serves as an ideal platform for critical applications in quantum sensing and quantum precision measurements due to its unique characteristics of compactness and robustness. Unlike the case of optical molasses or magneto-optical trapping (MOT), its operation requires neither careful alignment of cooling lasers nor presence of magnetic gradient field.
The research group designed and demonstrated a special form of isotropic laser cooling system for applications in quantum sensing. The diffused cooling optical field is generated by hollow laser beam injection while the frequency and power stability of probe laser is improved, so that the signal-to-noise ratio of the detection signal receives significant enhancement. Based on this experimental system, the researchers measured a series of basic characteristics of isotropic laser cooling in detail, and through the combination of experimental results and theoretical calculations, the basic physical process of isotropic laser cooling in this experimental system is quantitatively described and thoroughly understood. In particular, the effective intensity of the intracavity diffuse reflection optical field is precisely inferred, which is a parameter difficult to directly measure.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China; National Key Research and Development Program of China; Chinese Academy of Sciences; China Manned Space Engineering Office.
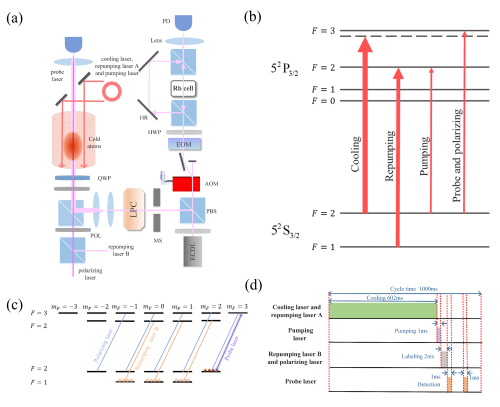
Fig. 1. Schematic diagrams of experimental setup and time sequence. (Image by SIOM)
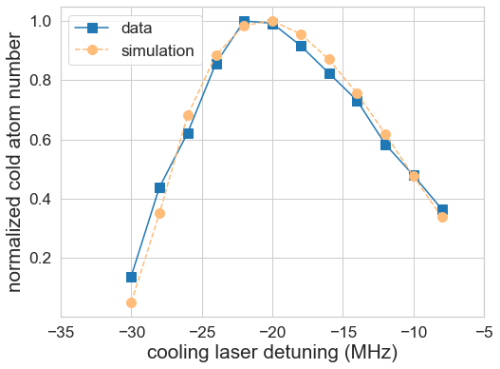
Fig. 2. Calculate the effective saturation factor of the intracavity diffuse reflection optical field according to the relation between the normalized cold atom number and the detuning of cooling laser. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.445877
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/