Recently, the Thin Film Optics Laboratory of Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the team of Professor Xiaoming Wei of South China University of Technology have made new progress in the compensation of intracavity dispersion in high-repetition ultrafast fiber lasers. The relevant results have been published on Optics Express on December 20, 2021.
High repetition frequency ultrafast fiber lasers are widely used in bio-optics, wave crest multiplexing systems, optical frequency combs and other fields. For ultrafast laser systems, dispersion compensation is essential. Dispersion compensation fibers and photonic crystal fibers are all-fiber dispersion compensation components commonly used in fiber lasers. The use of fiber for dispersion compensation is suitable for long cavity oscillators. For high repetition frequency and short cavity systems, the unit dispersion compensation capability of the fiber is weak, so a longer fiber is required. However, the propagation of high-energy lasers in a long fiber will accumulate strong nonlinear effect, leading to pulse distortion.
The researchers proposed a multifunctional dispersive mirror (MFDM) deposited on the fiber tip. The MFDM combines an anti-reflection structure, a quarter-wavelength structure and a cavity structure to remain high transmittance in pump wavelength and control the reflectivity and dispersion in working band. It is successfully prepared to provide more than 99% transmittance at the pump wavelength (976 nm), 93±2% reflectance at the laser excitation wavelength (1,050–1,060 nm) and negative dispersion of -5,000 fs2. The MFDM was successfully applied to the fiber laser oscillator as the input mirror, the output mirror and the dispersive mirror at the same time, and the ultrafast seed pulse with the Fourier transform limit of 364 fs was obtained. This kind of MFDM opens up a new research path for the development of compact high repetition frequency fiber lasers.
This work was supported by National Key R&D program of China; National Natural Science Foundation of China; Shanghai Sailing Program; NSAF Fund Jointly set up by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Engineering Physics; the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS; the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
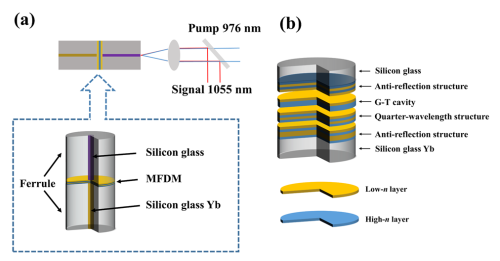
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic diagram of the MFDM application; (b) Schematic diagram of the MFDM structure. (Image by SIOM)
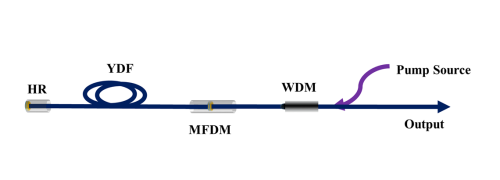
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of high repetition frequency fiber laser device. (Image by SIOM)
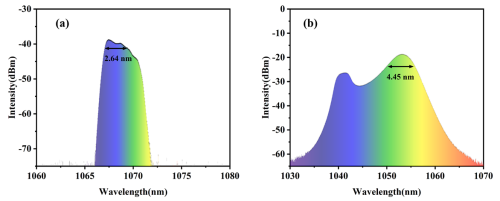
Fig. 3. (a) Spectral width before dispersion compensation; (b) Spectral width after dispersion compensation. (Image by SIOM)
Article Website:
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.441997
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/