Yb3+-doped large mode silica fiber is the most significant gain medium of high-power fiber lasers. However, the most serious issue at present is how to control its laser mode stability at a high output level.
Therefore, it becomes the research thrust to lower the refractive index (RI) difference between the core and cladding glasses meanwhile to keep it constant. In the past research, RI difference was often found to dramatically change during the fiber drawing and thermal annealing procedures, thus the laser beam quality deteriorated.
However, the underlying reasons why RI changes are unclear, and no valid way was proposed to solve this problem.
Recently, in order to explore further, a research team led by prof. Hu Lili from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) disclose the direct relationship among the thermal history, RI and structures of Heraeus F300 and Yb3+/Al3+/P5+/F--co-doped silica glasses (YbAPF) by the advanced solid state nuclear magnetic resonance techniques combining with vibration spectra. The study has been published in Journal of the American Ceramic Society on Mar. 11, 2021.
Through in-depth experimental analysis, the researchers have found that the RI change of YbAPF glass with different thermal histories is inextricably linked to the change of AlPO4 domains, the coordination number of the Al and Si-O-Si rings. Such a comprehensive study affords a significant reference for the precious manipulation of the numeral aperture of the Yb3+-doped active fiber.
Meanwhile, the researchers propose an innovative and effective way to greatly improve the beam quality of the large mode area photonic crystal fiber by proper thermal annealing.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Shanghai International Cooperation Fund, and the Shanghai Sailing Program.
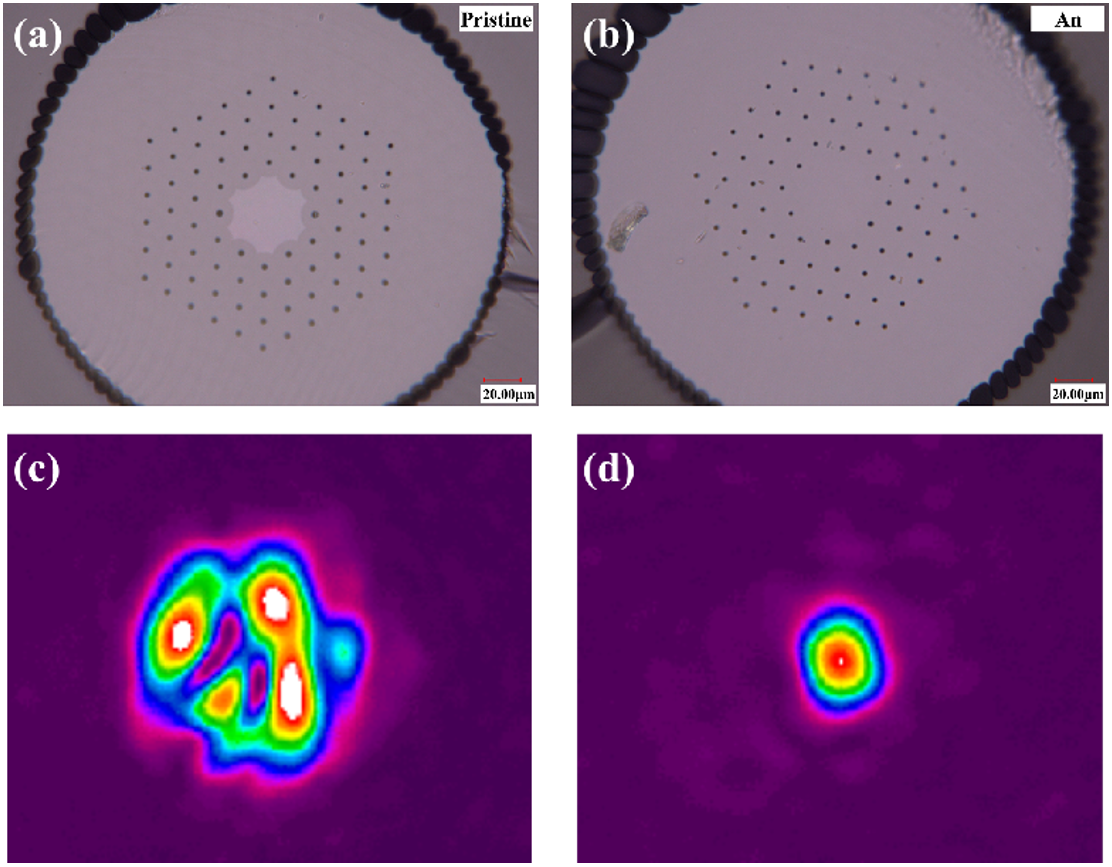
Microscopic images of the (a) pristine and (b) annealed LMA PCF cross sections. Laser beams of the pristine (c) and annealed (d) LMA PCF fibers. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17777
Contact:
WU Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn
Web: http://english.siom.cas.cn/