Visible luminescence of Tb3+ ions doped materials has found various applications in display techniques, visible light communication and medical treatment. Fluoride glasses are commonly used as a host material for gain fiber due to their low-energy phonon distribution. Unfortunately, poor chemical and mechanical properties, fabrication difficulties and expensive cost limit their development and further applications.
Most recently, a research team led by Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has succeeded in strengthening the absorption of Tb3+ ions by introducing Dy3+ sensitizer in phosphate glasses. The study was published in Journal of the American Ceramic Society.
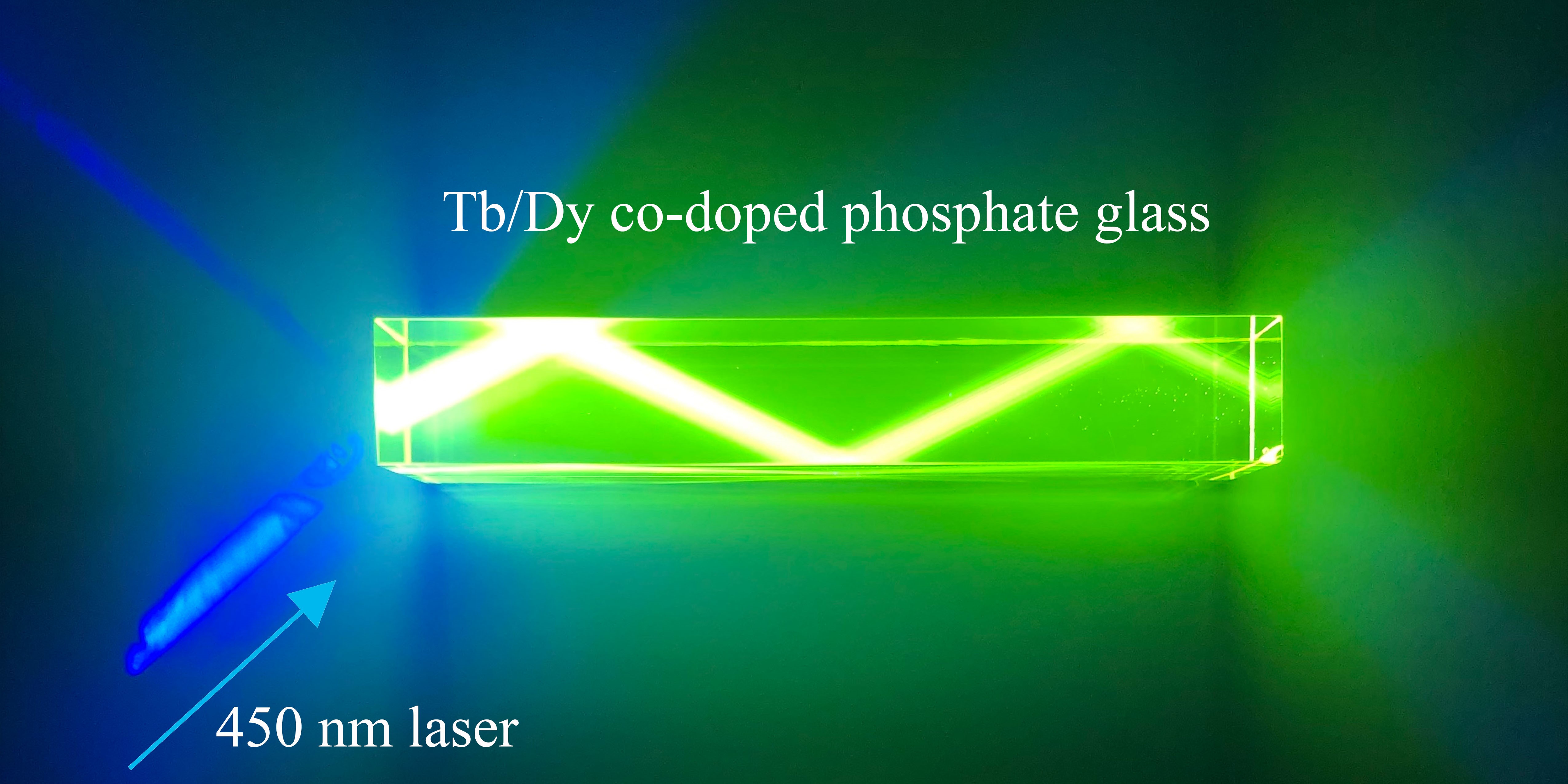
In their experiment, Tb3+/Dy3+ co-doped phosphate glasses were synthesized as a function of Dy3+ ions concentration by mature processing techniques. The element distributions, phases, absorption, emission spectra, and fluorescence lifetimes of Tb3+ and Dy3+ ions, as well as the energy transfer mechanisms were characterized and investigated. Homogeneous element distributions and uniform non-crystalline phases demonstrated a good quality of their phosphate glasses.
They found that large Judd–Ofelt parameters Ω2 and Ω4/Ω6 for Tb3+ ions could reach up to 21.60 × 10–20 cm2 and 0.73, respectively. Efficient sensitizer of Dy3+ for visible emission of Tb3+ was demonstrated, and a maximum energy transfer efficiency 55.0% for 4:0.5 ratio of Tb3+/Dy3+ at 425 nm wavelength for pumping was found.
Moreover, as a long lifetime of fluorescence decay is favorable for more efficient laser operation, a longest lifetime (2.86 ms) of Tb3+: 5D4 level in Tb3+/Dy3+ co-doped doped phosphate glasses was measured, which was much higher than those in other kinds of glasses.
This research may lead to a host material for fiber laser operated at visible wavelength.
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai.
Article website:
https://ceramics.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jace.17391
Contact:
Mr. Wu Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn