Recently, researchers from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics cooperating with the researchers from State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials in Shandong University have made new progress in the defect-induced damage behaviors of ADP crystals by 355nm pulsed laser. The related achievement has been published in [Optics Express, vol. 28, No.13, 18814-18828 (2020)].
ADP (NH4H2PO4) crystals are one kind of nonlinear optical material with excellent properties. Compared with KDP (KH2PO4) crystals, ADP crystals show larger effective nonlinear coefficients, higher laser induced damage thresholds (LIDT), especially at short wavelengths, and can be obtained in large size.
Besides, non-critical phase matching quadruple frequency can improve the laser output energy and reduce the phase mismatch caused by dispersion, being a potentially feasible technical route. Therefore, ADP crystals have great potential in short-wavelength applications in high power laser systems. It is of considerable significance to investigate the laser induced damage (LID) properties of ADP crystals in high power short wavelength lasers.
The research team succeeded in growing the ADP single crystals with medium size by Z-seed and directional seed rapid growth methods, as shown in figure 1.
By comparing with the LID characteristics under 355nm laser irradiation of ADP crystals grown in different growth methods, they found that the quality of crystals grown by conventional method is obviously better than that of crystals grown by point-seed rapid growth method. The types, quantity and density of defects in the pyramidal and prismatic sectors of ADP crystals are in discrepancy, resulting in the significant three times difference in laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) of the two growth sectors.
At the same time, the study showed that there are three types of “precursors” in ADP crystal via the initial LIDTs, and the ranges of initial LIDTs are 1-5J/cm2 (L defect), 6-12J/cm2 (M defect) and > 14J/cm2 (H defect), respectively. Only M defects and H defects exist in ADP crystal grown by the conventional method, and the rapid growth ADP crystals contain all the three types of defects. Laser conditioning can partially eliminate or modify L defects and M defects, thus increasing the LIDT of crystals.
They also discovered that these three types of "precursors" are a collection of a series of defects by means of spectral tests and the in-situ scattering measurements shown in figure 2.
This study can provide important ideas and references for the research and improvement of laser induced damage properties of ADP crystals and other nonlinear optical crystals.
The related work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11874369 and U1831211) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB1603).
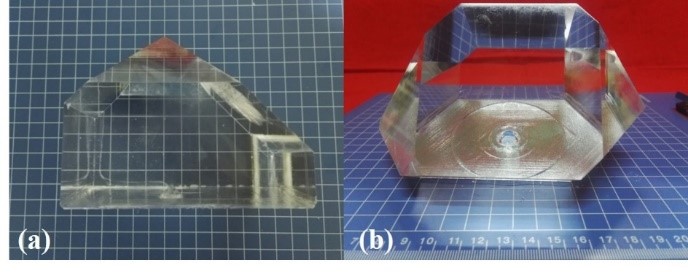
Fig. 1 The rapid growth ADP crystals (a) in Z direction and (b) in defined direction. (Image by SIOM)

Fig. 2 Typical morphology changes of in-situ scattering of ADP crystals with directional seed growth. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/abstract.cfm?uri=oe-28-13-18814&origin=search
Contact:
Mr. Wu Xiufeng
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: xfwu@siom.ac.cn