In the past decade, anti-resonant hollow-core photonic crystal fibers (HC-PCFs) have become excellent platforms for studying ultrafast nonlinear optics such as ultrashort pulse compression to the single-cycle regime, efficient generation of tunable dispersive wave (DW) at deep and vacuum ultraviolet wavelengths and soliton-plasma interactions. Although the transmission window of anti-resonant HC-PCF is disrupted by the presence of several sharp resonances, the appearance of these resonance bands gives rise to a new approach to high-efficiency emission of narrow-band DW. However, the high-efficiency DW generation can be achieved only when the wavelengths of the pump pulses are close to the resonance bands of the anti-resonant fibers.
Recently, the research group from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made new study on high-efficiency emission of dispersive wave. They demonstrated that photoionization effect of the pump pulse could greatly enhance the phase-matched DW emission within the resonance band of a gas-filled HC-PCF. The results were published in Optics Express.
The research group has carried out a series of theoretical and experimental studies on soliton-plasma interaction, including the generation of wavelength-tunable blueshifting soliton and the investigation of adiabatic soliton compression process. In this study, researchers obtained high-efficiency emission of dispersive wave in the resonance band through plasma-driven blueshifting soliton.
In the experiments, they observed that, as the pulse energy increased, the pump pulse gradually shifted to shorter wavelengths due to soliton-plasma interactions. When the central wavelength of the blueshifting soliton was close to the resonance band of the HC-PCF, high-efficiency energy transfer from the pump light to the DW in the visible region could be obtained.
During this DW emission process, the spectral center of the DW gradually shifted to longer wavelengths, leading to a slightly-increased DW bandwidth, which could be well explained as the consequence of phase-matched coupling between the pump pulse and the DW. In particular, at an input pulse energy of 6 μJ, the spectral ratio of the DW at the fiber output was measured to be as high as ~53%, corresponding to an over-all conversion efficiency of ~19%.
These experimental results, well accompanied by theoretical simulations and analysis, offer a practical and effective method of generating high-efficiency tunable visible light sources and provide insights into soliton-plasma interaction and resonance-induced DW emission.
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality; Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader; National Natural Science Foundation of China; Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
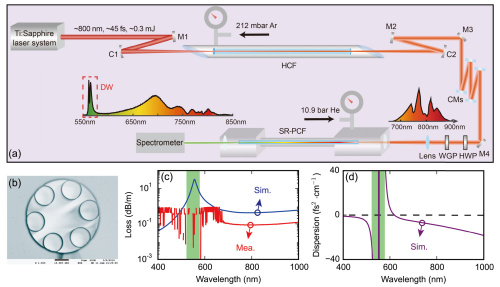
(a) Schematic of the experimental set-up. (b) SEM of the SR-PCF. (c) Measured and simulated fiber losses of the SR-PCF. (d) Simulated dispersion of the SR-PCF. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.393959
Contact:
Mr. CAO Yong
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: caoyong@siom.ac.cn