The tunable metamaterial absorbers in the mid-infrared spectral region are of great significance for thermal imaging, infrared camouflage, chemical sensing and radiation cooling. Current tunable metamaterial absorbers commonly introduce functional materials to achieve dynamic modulation of absorption properties. Among them, Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST)-based absorbers have attracted much attention for their excellence in tunable and efficient absorption. However, most work is centered on single frequency narrow-band absorption, and the analyses of absorption mechanism are still in the stage of theoretical simulation and therefore need further experimental images to validate.
Recently, the research team led by Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, had jointly demonstrated an active broadband tunable metamaterial absorber based on GST and used interferometric near-field scanning optical microscopy to investigate the near-field optical signals. Their study was published on RSC Advances.
In their study, the absorber was constructed by a metal double-sized unit cell and a metallic mirror separated by a thin GST spacer. To clearly obtain the physical images, a hybrid unit cell consisting of four square resonators was used to produce two absorption peaks. The experimental measurements showed that the absorber achieved broad working band covering mid-infrared range from 7.7μm to 8.5μm when the GST was in amorphous phase and the absorption bands redshift after GST was switched to the crystalline phase.
More importantly, the absorption mechanism was revealed by experimental near-field amplitude and phase images obtained from phase-resolved scanning near-field optical microscopy. The experimental near-field optical signals of absorber provide direct evidence that the broadband absorption is owing to the multi-resonant mode excited by the hybrid unit cell.
Their results will pave the way for the fundamental science field and have wide prospect for tunable absorption control applications.
These works were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Top-notch Talent Support Program in Shanghai, Shanghai Rising-Star Program and Shanghai Sailing Program and Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS.
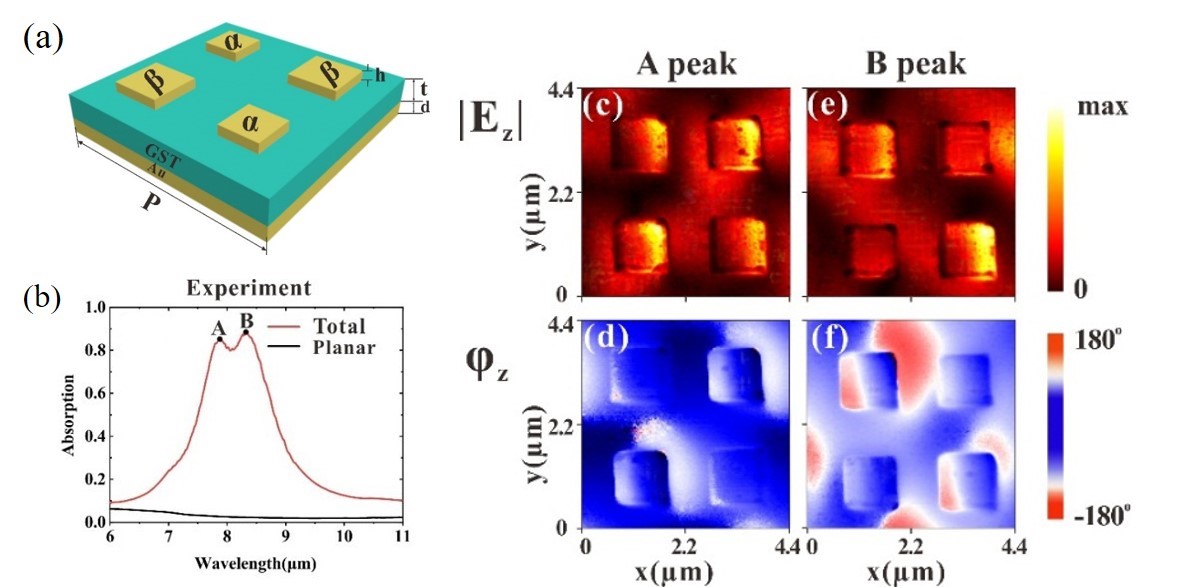
Schematic of the absorber with near-field amplitude and phase images at the absorption peaks (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/RA/C9RA10233G#!divAbstract
Contact:
Mr. CAO Yong
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: caoyong@siom.ac.cn