We are seeing an increasing demand for laser-resistant mirror coatings in inertial confinement fusion, extreme light infrastructure and other laser applications. The ideal UV laser mirror (UVLM) coating requires high reflectivity with large bandwidth and high laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT). Unfortunately, these requirements are difficult to achieve simultaneously. Traditionally, UVLMs are realized by deposition of laser-resistant layers on high reflective layers. However, compromises are made for the seemingly contradictory requirements.
Recently, scientists from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of New Mexico, had cooperatively proposed a “reflectivity and laser-resistance in one” design by using tunable nanolaminate layers with co-evaporated interfaces (NLD coating). The work was published in Light: Science & Applications.
In their experiment, an Al2O3-HfO2 nanolaminate-based mirror coating for UV laser applications was demonstrated using e-beam deposition. The bandwidth, over which the reflectance was larger than 99.5%, was more than twice that of a traditional “reflectivity bottom and LIDT top” combination design (TCD coating) mirror of comparable overall thickness. They found that the LIDT was increased by a factor of ~1.3 for 7.6 ns pulses at a wavelength of 355 nm.
In this study, the proposed new structure replaced the high-n materials in the traditional designs. The method enabled UVML coatings with larger high reflectivity bandwidth, higher LIDT and smaller transmission ripples in the VIS-NIR region compared to traditional designs of comparable overall thickness. The e-beam deposited nanolaminate materials could be used for large-size (meter-scale) UVML coatings.
Scientists believe that the described concept opens new avenues for improved UV coatings and can benefit many areas of laser technology that rely on high-quality optical coatings.
This research was supported by National Special Support Program for Young Top-notch Talent, National Natural Science Foundation of China, Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Shanghai Young Top-notch Talent Program.
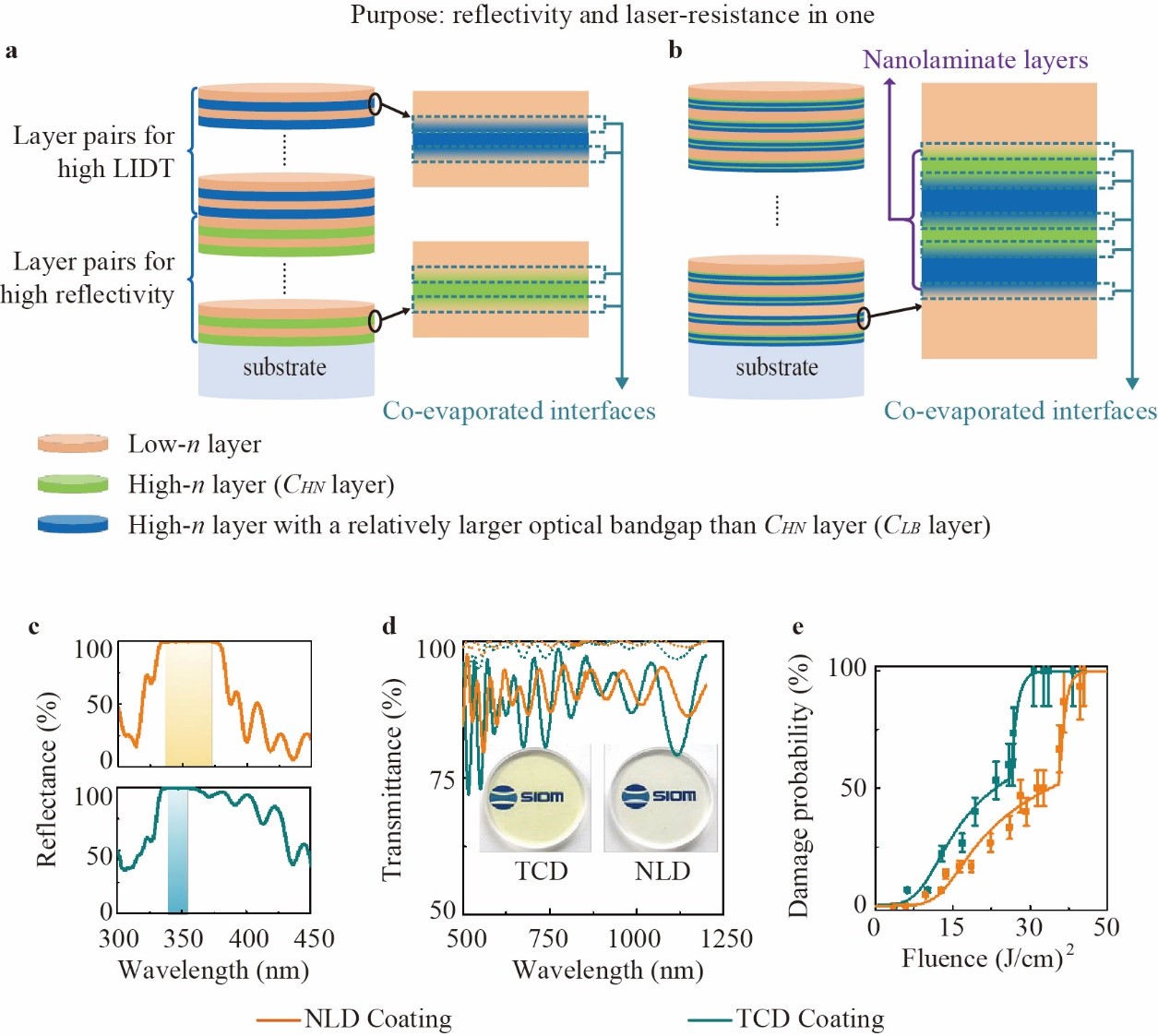
Schematic diagram and performance of the nanolaminate-based design for HR mirrors with high LIDT. (Image by SIOM)
Article website:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-020-0257-4
Contact:
Mr. CAO Yong
General Administrative Office
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, CAS
Email: caoyong@siom.ac.cn