Laser-induced defects can be created in the fused silica by irradiation with ArF excimer laser mainly via two photon absorption processes, which are evidenced by the observation that the concentration and absorption intensity of the laser-induced defects increase as a function of the laser power squared. However, compared to other wavelength laser sources, all three typical fluorescence bands of fused silica irradiated by ArF laser are still not reported simultaneously. Specifically, angular distribution of fluorescence bands has not been examined before.
Researchers at Research Center of Space Laser Information Technology——Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fines Mechanics (SIOM/China) studied laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) of high-purity fused silica irradiated by ArF excimer laser[JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 110, 013107 (2011)].
The results show that, for all the laser irradiation and observation conditions, laser modified fused silica exhibits intense broad fluorescence bands due to non-bridging oxygen hole centers(at 650 nm) and oxygen-deficiency centers (at 281 nm and 478 nm). Furthermore, LIF spectra of the fused silica characterize with angular distribution. Microscopic image of laser modified fused silica shows that laser-induced damage sites are responsible for enhanced light scattering of LIF. Finally,higher power density gives rise to a more intense fluorescence signal of the fused silica. The slopes of LIF signals are close to 2, which indicate that two-photon absorption processes dominate the formation of laser-induced defects. These results may have important implications for controlling and mitigation of laser-induced damage in fused silica.
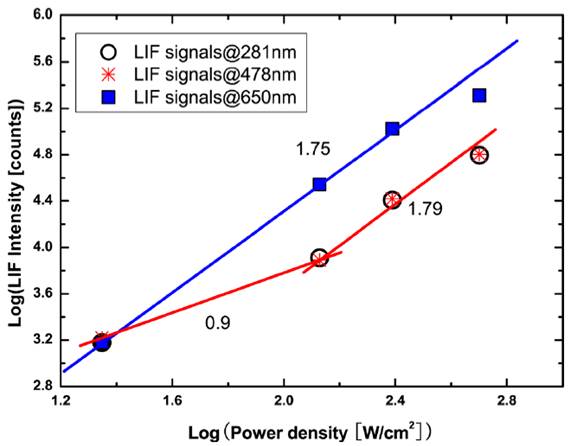 |
FIG. LIF signal intensity of the fused silica vs laser power density for ArF laser irradiation